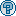
La función
Console.ReadLine() tiene implícito ese límite de 256 caracteres (254 sin
CarriageReturn +
LineFeed). Ese es el límite del tamaño del búfer del que hace uso al adquirir el flujo de entrada estándar o
std-in especificado en la función
Console.OpenStandardInput.
Puedes incrementar dicho límite a 32.767(-2) caracteres de la siguiente manera:
Console
.SetIn(new StreamReader
(Console
.OpenStandardInput(Int16
.MaxValue), Console
.InputEncoding,
false, Int16
.MaxValue));
O a 65.535(-2) caracteres si lo prefieres:
Console
.SetIn(new StreamReader
(Console
.OpenStandardInput(UInt16
.MaxValue), Console
.InputEncoding,
false, UInt16
.MaxValue));
El límite máximo teórico es
Int32.MaxValue (
Maximum length of byte[]? +
<gcAllowVeryLargeObjects> element ), pero llegar a esos extremos para este tipo de escenario lo veo totalmente innecesario.
La llamada al método
Console.SetIn() puedes acomodarlo de forma reutilizable como en el siguiente ejemplo de
clase, y simplemente llamar al método
SetInBufferSize() cuando sea necesario:
Public NotInheritable Class ConsoleUtil
#Region " Constructors "
''' ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
''' <summary>
''' Prevents a default instance of the <see cref="ConsoleUtil"/> class from being created.
''' </summary>
''' ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
<DebuggerNonUserCode>
Private Sub New()
End Sub
#End Region
#Region " Private Members "
''' <summary>
''' The underlying standard input stream (stdin) used for <see cref="ConsoleUtil.SetInBufferSize"/> method.
''' </summary>
Private Shared stdIn As StreamReader
#End Region
#Region " Public Methods "
''' ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
''' <summary>
''' Sets the buffer size of the standard input stream (std-in)
''' acquired from the <see cref="System.Console.OpenStandardInput"/> function.
''' <para></para>
''' So the <see cref="Console.ReadLine()"/> function can benefit from a larger buffer size.
''' <para></para>
''' Default buffer size is 256.
''' </summary>
''' ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
''' <param name="bufferSize">
''' Minimum value is: 256.
''' <para></para>
''' Note that the last two characters in the buffer are reserved for
''' <see cref="ControlChars.Cr"/> + <see cref="ControlChars.Lf"/>.
''' </param>
''' ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
<DebuggerStepThrough>
Public Shared Sub SetInBufferSize(bufferSize As Integer)
If bufferSize < 256 Then
Throw New ArgumentException(NameOf(bufferSize), message:="Value must be equal or greater than 256.")
End If
ConsoleUtil.stdIn?.Close()
ConsoleUtil.stdIn = New StreamReader(Console.OpenStandardInput(bufferSize), Console.InputEncoding, False, bufferSize)
Console.SetIn(ConsoleUtil.stdIn)
End Sub
#End Region
End Class
#End Region
Traducción a C#:
public sealed class ConsoleUtil {
#region Constructors
/// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/// <summary>
/// Prevents a default instance of the <see cref="ConsoleUtil"/> class from being created.
/// </summary>
/// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[DebuggerNonUserCode]
private ConsoleUtil() { }
#endregion
#region Private Members
/// <summary>
/// The underlying standard input stream (stdin) used for <see cref="ConsoleUtil.SetInputBufferSize"/> method.
/// </summary>
private static StreamReader stdIn;
#endregion
#region Public Methods
/// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/// <summary>
/// Sets the buffer size of the standard input stream (std-in)
/// acquired from the <see cref="System.Console.OpenStandardInput"/> function.
/// <para></para>
/// So the <see cref="Console.ReadLine()"/> function can benefit from a larger buffer size.
/// <para></para>
/// Default buffer size is 256.
/// </summary>
/// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/// <param name="bufferSize">
/// Minimum value is: 256.
/// <para></para>
/// Note that the last two characters in the buffer are reserved for
/// <see cref="ControlChars.Cr"/> + <see cref="ControlChars.Lf"/>.
/// </param>
/// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[DebuggerStepThrough]
public static void SetInBufferSize(int bufferSize) {
if (bufferSize < 256) {
throw new ArgumentException
(nameof
(bufferSize
), message
:"Value must be equal or greater than 256."); }
ConsoleUtil.stdIn?.Close();
ConsoleUtil
.stdIn = new StreamReader
(Console
.OpenStandardInput(bufferSize
), Console
.InputEncoding,
false, bufferSize
); Console.SetIn(ConsoleUtil.stdIn);
}
#endregion
}
#endregion
----------------------
Como alternativa a lo de arriba, en caso de que prefieras no reemplazar el flujo de entrada estándar, puedes definir una función como esta de aquí abajo, que puedes añadir a la clase de arriba, para que sirva como reemplazo de la función
Console.ReadLine().
VB.NET:
''' ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
''' <summary>
''' Reads the next line of characters from the standard input stream.
''' <para></para>
''' This function attempts to be a improved replacement for <see cref="System.Console.ReadLine()"/> function.
''' </summary>
''' ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
''' <param name="bufferSize">
''' The character limit to read in the next line of characters from the standard input stream.
''' <para></para>
''' Minimum value is: 256.
''' <para></para>
''' Default value is: <see cref="Short.MaxValue"/> (32767).
''' <para></para>
''' Note that the last two characters in the buffer are reserved for
''' <see cref="ControlChars.Cr"/> + <see cref="ControlChars.Lf"/>.
''' </param>
''' ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
''' <returns>
''' The next line of characters from the input stream,
''' or <see langword="Nothing"/> if no more lines are available.
''' </returns>
''' ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
<DebuggerStepThrough>
Public Shared Function ReadLine(Optional bufferSize As Integer = Short.MaxValue) As String
If bufferSize < 256 Then
Throw New ArgumentException(NameOf(bufferSize), message:="Value must be equal or greater than 256.")
End If
Dim inputStream As Stream = Console.OpenStandardInput(bufferSize)
Dim bytes(bufferSize - 1) As Byte
Dim outputLength As Integer = inputStream.Read(bytes, 0, bufferSize)
Dim chars As Char() = Console.InputEncoding.GetChars(bytes, 0, outputLength)
Return New String(chars).TrimEnd({ControlChars.Cr, ControlChars.Lf})
End Function
Traducción a C#
/// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/// <summary>
/// Reads the next line of characters from the standard input stream.
/// <para></para>
/// This function attempts to be a improved replacement for <see cref="System.Console.ReadLine()"/> function.
/// </summary>
/// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/// <param name="bufferSize">
/// The character limit to read in the next line of characters from the standard input stream.
/// <para></para>
/// Minimum value is: 256.
/// <para></para>
/// Default value is: <see cref="Short.MaxValue"/> (32767).
/// <para></para>
/// Note that the last two characters in the buffer are reserved for
/// <see cref="ControlChars.Cr"/> + <see cref="ControlChars.Lf"/>.
/// </param>
/// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/// <returns>
/// The next line of characters from the input stream,
/// or <see langword="Nothing"/> if no more lines are available.
/// </returns>
/// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[DebuggerStepThrough]
public static string ReadLine(int bufferSize = short.MaxValue) {
if (bufferSize < 256) {
throw new ArgumentException
(nameof
(bufferSize
), message
:"Value must be equal or greater than 256."); }
Stream inputStream = Console.OpenStandardInput(bufferSize);
byte[] bytes
= new byte[bufferSize
]; int outputLength = inputStream.Read(bytes, 0, bufferSize);
char[] chars = Console.InputEncoding.GetChars(bytes, 0, outputLength);
return (new string(chars
)).TrimEnd(new[] {'\r',
'\n'}); }
Modo de empleo en C#:
// Copy very long string to clipboard.
string longString
= new string('0',
short.MaxValue); Clipboard.SetText(longString);
// Manually paste the string here...
string line = ConsoleUtil.ReadLine(bufferSize:ushort.MaxValue);
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine($"String Length: {line.Length}");
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to exit...");
Console.ReadKey();
Environment.Exit(0);




 Autor
Autor


 En línea
En línea